Cost of Revenue & SaaS Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
What Is Cost of Revenue?
The cost of revenue is the total price of creating and delivering a product or service to a customer. For SaaS companies, this includes hosting fees, server and cloud space, website development and maintenance costs, software license agreements, and the salaries of the customer support team.

Categories
Table of Contents
What Is Cost of Goods Sold?
Cost of goods sold refers to the direct costs of producing the product or delivering a service. It typically includes direct labor costs, direct material costs, overhead costs, and other production process costs.
COGS for a SaaS company follows the same principle of including direct costs. However, a SaaS business model requires additional costs to render the service. For instance, you need to include costs for customer support and account management as they’re part of the service.
In other words, you should include costs you incur to offer and support the product or service. Here are the typical costs SaaS companies include in COGS:
- Application hosting costs — how much you pay for Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Customer support, personnel training, and account management costs
- Software fees for applications used directly within the product
- Website development and support
- Other indirect expenses related to creating or maintaining the product or service
Including indirect costs in COGS helps ensure that you have a fully-burdened, accurate cost of revenue. The customer success team, for example, supports retention and expansion efforts. Customer success managers loop the sales team into any upsell and cross-sell agreements, as well as help optimize services according to the customers’ growing needs as the relationship grows. Any time the sales team spends on updating contracts also falls under SaaS COGS.
SaaS Cost of Revenue vs. Cost of Goods Sold
The difference between cost of revenue and COGS is that cost of revenue is COGS plus distribution and marketing costs. To take this distinction a step further, your cost of revenue includes all the costs the company incurs to obtain a sale (which includes any fixed costs or variable costs) plus the cost of goods sold.
For other types of companies, like ecommerce businesses or retailers, the costs incurred to obtain a sale are necessary for producing the product. For example, companies with a physical product need to account for raw material, labor, shipping costs, and production costs. Customer support doesn’t impact COGS, which is why these companies categorize it as an operating expense. SaaS companies, meanwhile, include customer support costs to their cost of revenue since customer support is essential and directly related to providing and maintaining the product or service.
Get The 10 SaaS Metrics You Didn’t Know You Needed
How to Calculate SaaS COGS
While COGS and cost of revenue may be slightly interchangeable, the formulas are not. The below formula offers how most product-based companies calculate their COGS:

To calculate COGS, add the cost of the inventory you start with and the direct expenses you incur during a given period. Then, subtract the inventory you’re left with at the end of the reporting period.
Since SaaS companies offer software as a service, the formula isn’t applicable. Instead, they sum up all the direct costs of offering their service.
For example, here’s what Slack included in its cost of revenue or SaaS COGS calculation while preparing its income statement for the first quarter of 2022:

Image sourced from Q1 financial statements for 2022 from Slack Technologies.
In other words, there’s no single formula you can use to calculate SaaS COGS. It’s simply a sum of direct costs — which may differ among SaaS companies.
Why Cost of Revenue Is Important for SaaS Businesses
Cost of revenue provides critical insight into a company’s financial health. It helps you calculate the company’s gross profit and gross profit margin, which in turn enables you to assess overall profitability using the rule of 40.
Besides that, the costs included in the cost of revenue for SaaS companies are more diverse than for companies in other industries. Those costs can significantly fluctuate and shrink (or expand) your gross margins.
Slack’s financial statements serve as a prime example of how costs impact gross margin. Slack’s SEC filings don’t provide a complete breakdown of the total cost of revenue, but it provides insights into why its cost of revenue increased. It cites an increase in third-party hosting fees, personnel and related costs, and credit card payment processing fees as primary reasons for the increase in cost of revenue:

Image sourced from June 2021 Quarterly Report from Slack Technologies.
The increase in Slack’s cost of revenue can be directly traced back to its growth. But if the cost of revenue increases without significant returns in terms of growth, you need to break down these costs and find out what’s affecting your margins or financial efficiency.
Track Cost of Revenue (SaaS COGS) in Real Time with Mosaic
Tracking the cost of revenue in real time can feel like grunt work. Why spend hours tracking every facet of your cost of revenue and leaving it susceptible to human error when you can easily automate it?
Mosaic takes over tracking cost of revenue by integrating with your source systems to gather the information you need for a fully-burdened cost of revenue measurement. You can view your cost of revenue in real time and view an up-to-the-minute breakdown of any associated costs.
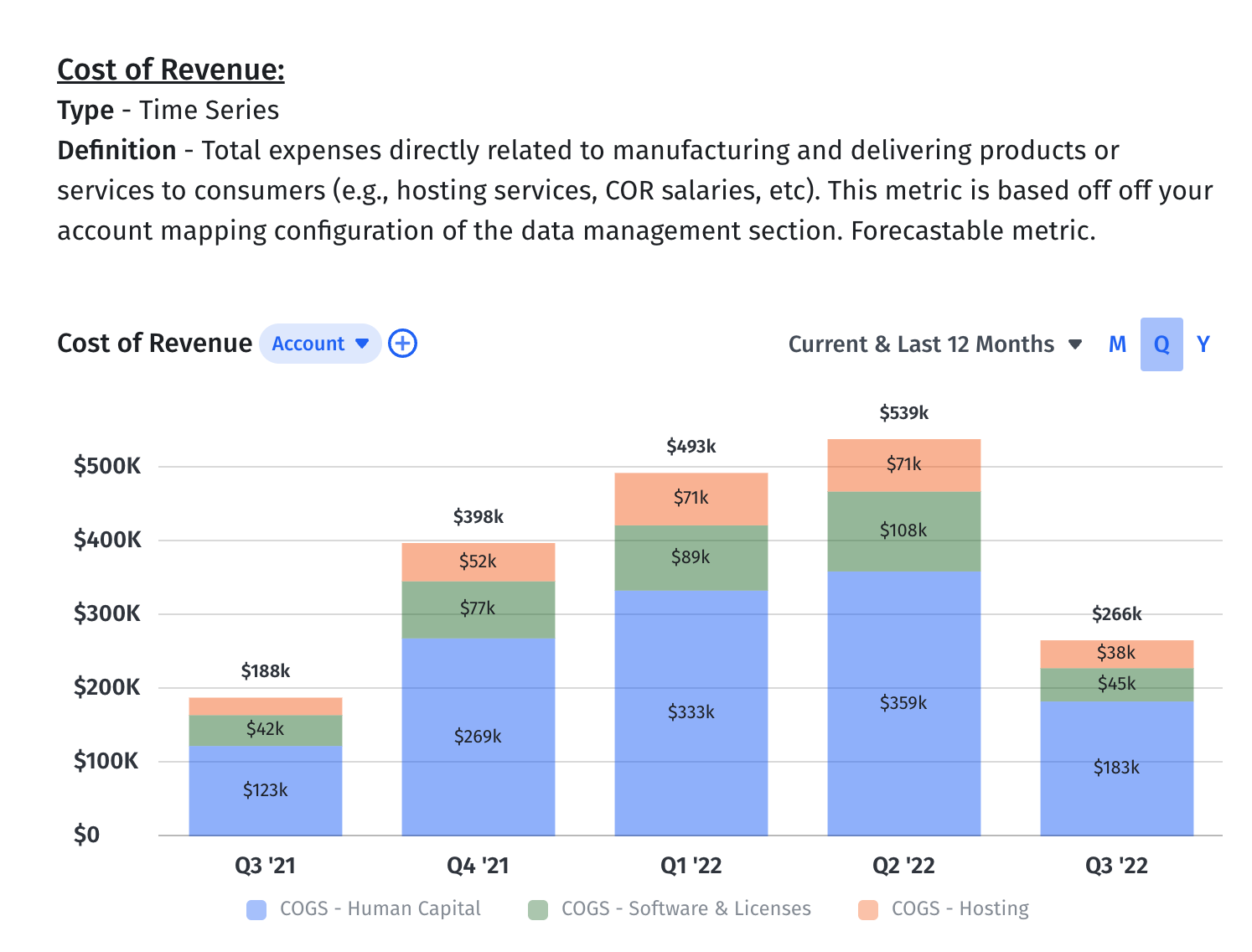
Mosaic offers a preloaded Variance Analysis template that allows you to immediately view your expenditures and total revenue in one location. Cost of revenue is its own line item in the “Expense Changes” table, which you can view in a monthly, quarterly, or annual view to track any changes and forecast trends.

You can also create a custom report, where you can include the metrics that matter to your business. Dive deeper into your cost of revenue data by tracking and automatically calculating the rule of 40, SaaS quick ratio, and annual recurring revenue (ARR) in one place. And when you include your sales performance metrics and customer retention metrics, you can prompt powerful dialogue and collaboration between departments to help drive your cost of revenue lower and help teams bolster their operational efficiency.
Learn how Mosaic can help you level up your financial reporting with a personalized demo.
How Strategic Finance Software Can Help Rev Ops Teams
Cost of Revenue FAQs
What is COGS in SaaS?
COGS in SaaS is the total of all costs related to creating and delivering the product or service to the customers. Typical costs include hosting fees, software license fees, server and cloud storage fees, website maintenance fees, and the customer support team’s salaries.
What is the cost of revenue formula?
Is cost of revenue an expense?
Can COGS be used for services?
Is cost of revenue the same as cost of goods sold?
Explore Related Metrics
Own the of your business.